One of the most important ways that the quality of an academic paper is measured is through its citations. Citations are a critical part of any paper as they indicate the sources that the writer referred to when writing and performing their research.
A well-researched paper will include high-quality citations so that others can easily understand how the author formed their understanding of the topic.
Citations also provide evidence of how deeply the author understands the main relevant discussions in their field. If you are writing an academic paper, citing high-quality sources is critical to having your own work recognized. But how can you rate the quality of a citation? There are a number of metrics used to evaluate citation quality.
Let’s look at how citation quality is measured, how important citation quality is to the impact factor of an academic publication, and some tools that can help you determine the quality of the sources you are citing.
Table of Content:
How is Citation Quality Measured?
One of the most common is simply how often a paper has been cited. Logically, we assume that academic work that becomes fundamental or famous in a particular field tends to have a very high citation rate. Thus, the more a paper is cited, the more central to the field it must be.
Citing a paper that many other people have cited before you shows that you are familiar with the authoritative voices in the literature. Proper citation also avoids the risk of plagiarism, which can risk your paper being retracted or not published at all if it is detected.
However, increasingly, publishers and authors are trying to consider other aspects when evaluating citation quality. One reason for this is that simply measuring by the number of citations can create a kind of self-reinforcing cycle.
One example is that Google Scholar organizes papers by the number of times they have been cited, so papers that have already been cited many times are more likely to be viewed, read, and cited again. Other considerations like language and regional biases can also influence how often a paper is cited.
So what other things should you consider when you are citing a source to determine its quality? In addition to how many other people have cited a source, you should consider how old the source is, whether it has been peer-reviewed, and whether it has been discredited or retracted.
In addition, you want to avoid relying too much on a particular journal or author in your research. Citing a balance of recent, peer-reviewed, recognized sources will improve the quality of your own research paper.
Avoiding Low-quality Citations
Even if you know what you’re looking for, it can be challenging to determine whether a source is high quality and worth citing in your paper. The nature of the internet means that even if a paper has been retracted or found fraudulent, it may still be easy to find and appear like a normal source in old journal editions.
Always check the status of an article on the publisher’s website to see if any announcements have been posted regarding the article you want to cite.
You should also do some research into the journal that published the article you want to cite. With pay-to-publish predatory journals on the rise, it’s easier than ever to accidentally cite sources that were not properly peer-reviewed.
Citing this kind of low-quality source in your paper can harm the credibility of your own argument and research, so make sure you are only citing work from reputable publications.
Finally, you should make sure that the source you are citing is the most up-to-date on the subject, and that you aren’t relying too much on the work of one journal or author in particular. Relying on out-of-date reference materials runs the risk of making your own work obsolete before it has even been published.
If you don’t address the latest developments on your topic in your own writing, your work will be of limited use to others. It is also key to avoid overusing one journal or author. Doing so makes it seem as though the amount of research you did was limited and that you aren’t aware of other relevant experts and research.
Save Yourself Some Time: Use a Citation Checker
It’s clear that identifying high-quality sources is a big task. Doing the necessary due diligence to ensure that you are only citing high-quality sources in your paper can add hours to the time needed to research. Fortunately, there are tools available to help you with this process.
While there are a number of citation checkers and reference managers available, many of them still have limited functionality when it comes to evaluating citation quality. This is because they rely on citation metrics alone to determine source quality.
Trinka, an AI writing assistant available at trinka.ai, is one of the rare citation checkers that can review citations not only for metrics, but also for journal overuse, age, retraction status, and journal or source quality.
Trinka offers comprehensive citation analysis reports for free. You can submit your paper to the Trinka citation analysis and it will highlight problematic citations in your work.
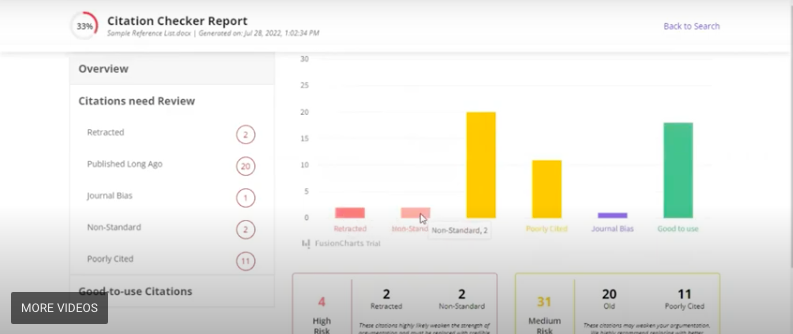
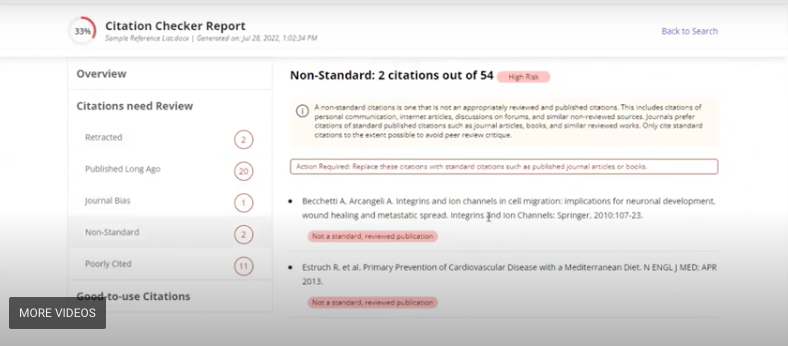
Any researcher or academic knows the importance of publishing, and citing quality sources is a great way to make sure that your work gets the recognition it deserves. Now, you can save yourself time and energy while still making sure that your work contains the highest quality of citations possible by using Trinka. Give it a try today.
Web Stories: